As a leading solar energy manufacturer, SolarCtrl equips global retailers and installers with high-quality, durable solar products. Our technology-driven solutions, rapid delivery, and robust support ensure your business thrives.
Discover SolarCtrl's comprehensive range of solar solutions tailored for efficiency and sustainability.
Our product lineup includes advanced solar inverters, high-efficiency solar panels, complete solar power systems, and a variety of other solar products.
Each category is designed to meet the diverse needs of our clients, ensuring reliability, durability, and optimal performance in all environmental conditions.
SolarCtrl enhances your business with streamlined services tailored for the solar energy industry. We offer flexible OEM solutions, efficient delivery, and dedicated after-sales support, all designed to elevate your operational success and customer satisfaction.
Empower your solar needs with our robust production capabilities, ensuring large-scale output and consistent quality to meet your demands efficiently.
Experience superior solar inverters, solar panels, and solar power systems, that deliver reliable performance and durability, all at a cost-effective price point.
Enhance your offerings with our customizable solar products, designed to meet specific requirements through our comprehensive OEM support.
Adaptable minimum order quantities coupled with rapid delivery options ensure you get what you need, when you need it.
Our solar products come with top industry certifications, offering you and your clients the assurance of safety and quality.
From pre-sales consultations to after-sales technical support, we’ve got you covered every step of the way.
Empower your solar needs with our robust production capabilities, ensuring large-scale output and consistent quality to meet your demands efficiently.
Experience superior solar inverters, solar panels, and solar power systems, that deliver reliable performance and durability, all at a cost-effective price point.
Enhance your offerings with our customizable solar products, designed to meet specific requirements through our comprehensive OEM support.
Adaptable minimum order quantities coupled with rapid delivery options ensure you get what you need, when you need it.
Our solar products come with top industry certifications, offering you and your clients the assurance of safety and quality.
From pre-sales consultations to after-sales technical support, we’ve got you covered every step of the way.
Explore our state-of-the-art Solar Panel Factory, where precision and quality meet sustainability.
Our production lines are equipped with the latest technology to manufacture solar panels that offer superior performance and long-lasting durability.
This facility is dedicated to producing environmentally friendly solutions that support the global shift towards renewable energy.
Take a closer look at our Solar Inverter Factory, a hub of innovation and efficiency.
Here, we specialize in crafting solar inverters that are not only robust and reliable but also optimized for varied climatic conditions.
Our advanced manufacturing processes ensure that each inverter meets the highest standards of quality and performance, empowering businesses and communities worldwide.
At SolarCtrl, we offer comprehensive Sourcing Combo services, providing a one-stop solution for all your solar product needs.
We pride ourselves on our strong partnerships with globally renowned brands such as Jinko Solar, JA Solar, LONGi, and Growatt.
These collaborations enable us to supply a broad spectrum of high-quality, cutting-edge solar products, ensuring you have access to the best the industry has to offer.
Navigate the complex world of solar energy with SolarCtrl’s Comprehensive Buyer’s Guide.
This detailed guide covers essential topics including basic solar knowledge, applications, cost analysis, certifications, current technologies, market trends, and tips for finding qualified suppliers.
Whether you’re new to solar solutions or looking to expand your expertise, our guide provides the insights you need to make informed decisions and optimize your solar investments.

Solar energy, harnessed from the sun’s radiant light and heat, offers a clean and inexhaustible energy source, making it a key component of sustainable solutions. It contrasts sharply with fossil fuels, which contribute to global warming and pollution.
Through technologies like photovoltaic panels and concentrated solar power systems, solar energy can be converted directly into electricity or used for heating. This renewable energy is versatile, eco-friendly, and increasingly affordable, significantly reducing our reliance on carbon-intensive sources.
1839: Edmond Becquerel, a French physicist, discovers the photovoltaic effect while experimenting with an electrolytic cell made up of two metal electrodes placed in an electrolyte solution. He observes that the cell produces more electricity when it is exposed to light.
1873: Willoughby Smith discovers the photoconductivity of selenium, laying the groundwork for solar cells.
1883: Charles Fritts, an American inventor, creates the first genuine solar cell by coating selenium with a thin layer of gold.

1954: Scientists at Bell Labs introduce the first silicon photovoltaic (PV) cell, capable of converting enough solar energy into power to run everyday electrical equipment. This breakthrough significantly advances the practical applications of solar energy.
1970s: The energy crisis in the United States drives substantial funding and research into solar energy, resulting in rapid efficiency improvements and the development of the solar technology used today.
1980s: Worldwide, solar technology begins to be installed at a commercial scale, particularly in remote areas, and for specialized applications such as satellites in space, where solar power is a practical solution for energy generation.
2000s and Beyond: Advances in technology have driven down the cost of solar panels and systems dramatically, making solar energy a competitive and sustainable energy source globally. Innovations such as thin-film solar cells, concentrated solar power, and solar thermal technology have diversified the applications of solar energy.
A typical solar energy system comprises several key components, each integral to transforming sunlight into usable electricity and managing its distribution.
Function: Solar panels are the most visible part of a solar energy system. They consist of multiple photovoltaic (PV) cells that capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. These cells are made from layers of semiconductor materials, typically silicon, which create an electric field that helps in the conversion process.
Varieties: There are different types of solar panels, primarily monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film, each with different efficiencies, costs, and applications.
Function: The inverter is a critical component that converts the DC electricity generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is the standard electrical form used by most home appliances and the power grid.
Types: There are several types of inverters, including string inverters, microinverters, and power optimizers. Each type has its specific advantages, such as efficiency in converting electricity, adaptability to shading, and ease of monitoring individual panel performance.
Function: Battery storage systems are used to store excess solar power generated during peak sunlight hours, which can then be used at night or during overcast days. This component is essential for maintaining a consistent power supply and maximizing the system’s self-consumption.
Types: Different technologies like lithium-ion, lead-acid, and saltwater batteries offer various capacities, lifespans, and cost profiles.
Function: A charge controller regulates the voltage and current coming from the solar panels to the battery. It protects the batteries from being overcharged and can significantly enhance the battery’s lifespan by preventing battery overvoltage.

Importance: This component is essential for maintaining battery health and efficiency, particularly in off-grid solar systems or systems with backup storage.
Function: The mounting system includes the racks and fixtures used to secure solar panels to the roof or the ground. This system ensures that panels remain stable and are angled to capture the optimal amount of sunlight.
Considerations: Factors such as wind load, roof slope, and orientation are critical when designing and installing the mounting system to maximize energy production and maintain structural integrity.
Function: Monitoring systems provide real-time data on the performance of the solar system. They help in tracking energy production, consumption, and the efficiency of solar panels and other components.
Capabilities: Modern monitoring systems can detect issues, provide maintenance alerts, and even forecast energy production based on weather predictions.
Includes: Wiring, fuses, junction boxes, disconnect switches, and grounding equipment are all necessary for safely conveying electricity from the solar panels to the inverter, to the electrical loads, and possibly back to the grid.
Safety and Compliance: These components must meet local electrical codes and standards to ensure safety and reliability.
Each of these components plays a vital role in the overall functionality and efficiency of a solar energy system. By working in concert, they not only convert solar energy into a usable form but also ensure that this energy is safely stored and efficiently used, contributing to the system’s effectiveness and the user’s energy independence.
Solar energy systems are primarily categorized into two types, each harnessing the sun’s power through different technological approaches:

Photovoltaic systems are the most common type of solar energy systems used in residential and commercial settings.
They consist of solar panels, or modules, made up of many solar cells containing semiconductor materials, typically silicon. When sunlight strikes these cells, it generates an electric field across the layers, causing electricity to flow.
PV systems are versatile and can be installed on rooftops, integrated into building facades, or mounted on the ground. They are scalable, ranging from small, rooftop systems generating a few kilowatts to large solar farms producing megawatts.

Concentrated Solar Power systems utilize mirrors or lenses to focus a large area of sunlight into a small beam, significantly intensifying the solar energy.
This concentrated light is then used to heat up a fluid, typically molten salt, which retains heat efficiently. The heat from the fluid is used to produce steam that drives a turbine connected to a generator, which produces electricity.
CSP systems are primarily used in large-scale solar power plants and are particularly beneficial in desert areas where sunlight is abundant. Unlike PV systems, CSP systems can store the solar energy thermally, allowing for power generation even after sunset.
Each system type has distinct characteristics and applications, with PV systems being more adaptable for decentralized setups like residential installations, and CSP systems more suited for centralized, utility-scale projects that contribute significantly to the power grid.
A solar energy system harnesses the sun’s energy and converts it into electricity that can be used in homes, businesses, and industries.
The process begins when sunlight falls on solar panels installed typically on rooftops or ground-based mounts. Each panel contains numerous photovoltaic (PV) cells made from semiconductor materials like silicon. These cells are designed to capture solar radiation (photons).
As the photons are absorbed by the photovoltaic cells, their energy causes electrons in the semiconductor material to become loose. These free electrons move through the material, creating a flow of electrical current. This is known as the photovoltaic effect. The current generated at this stage is direct current (DC).
The DC electricity produced by the solar panels is not directly usable by most home appliances or the electrical grid, which operate on alternating current (AC). Therefore, the DC electricity is directed from the panels to an inverter. This device converts the DC into AC, making it usable for household needs and compatible with the grid.
If the system includes battery storage, the AC can be converted back to DC to charge the batteries. This stored electricity can be used during times when the panels are not producing electricity, such as at night or during overcast days. In systems without batteries, the electricity goes directly to the power distribution panel.
From the inverter, the AC electricity flows to the building’s electrical panel, where it is distributed to different electrical circuits for use in lighting, appliances, and other devices.
In grid-connected systems, any excess electricity generated that is not immediately used can be sent back to the power grid. A utility meter monitors the amount of electricity sent to the grid and the electricity drawn from it. Many utilities offer net metering, which credits solar energy system owners for the electricity they add to the grid.
Solar energy is a compelling option for sustainable power production, but like any technology, it has its benefits and challenges. Here’s a look at the advantages and disadvantages of solar energy:

Solar energy is one of the most abundant natural resources, available nearly everywhere in the world. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite, solar energy can be harnessed without the fear of depletion, making it a crucial component in the transition to sustainable energy systems.
After the initial setup, solar panels generate electricity at no ongoing cost. This can significantly reduce electricity bills, especially in areas with high energy rates. Moreover, with net metering policies, homeowners can sell excess electricity back to the grid, often receiving credits or payments that further offset costs.
Solar energy systems are known for their durability and require minimal maintenance. Once installed, they can reliably produce power for 25 to 35 years. The main requirement is periodic cleaning of the panels to maintain efficiency and occasional checks of the inverter and other equipment.
The cost of purchasing and installing solar panels can be prohibitive, though it has decreased significantly over the years. This includes the cost of the panels, inverter, batteries (if needed), wiring, and installation labor.
Although solar panels can collect energy during cloudy and rainy days, their efficiency significantly drops compared to sunny days.
This variability can impact the reliability of solar as a sole energy source without adequate storage solutions.
To generate a substantial amount of energy, a considerable amount of surface area is required. This can be a limiting factor in urban areas or for businesses and homes with limited roof space.

While solar energy presents a promising and increasingly accessible option for clean, renewable energy, these factors must be considered when evaluating its suitability for specific applications and environments.
Solar energy systems have a wide range of applications, leveraging the sun’s power to provide clean, renewable energy in various sectors.
Solar panels are commonly installed on the roofs of homes and commercial buildings to provide a significant portion of their electricity needs. This not only reduces utility bills but also contributes to a building’s energy independence. In commercial settings, solar energy can power office buildings, warehouses, and retail stores, helping businesses reduce operational costs.
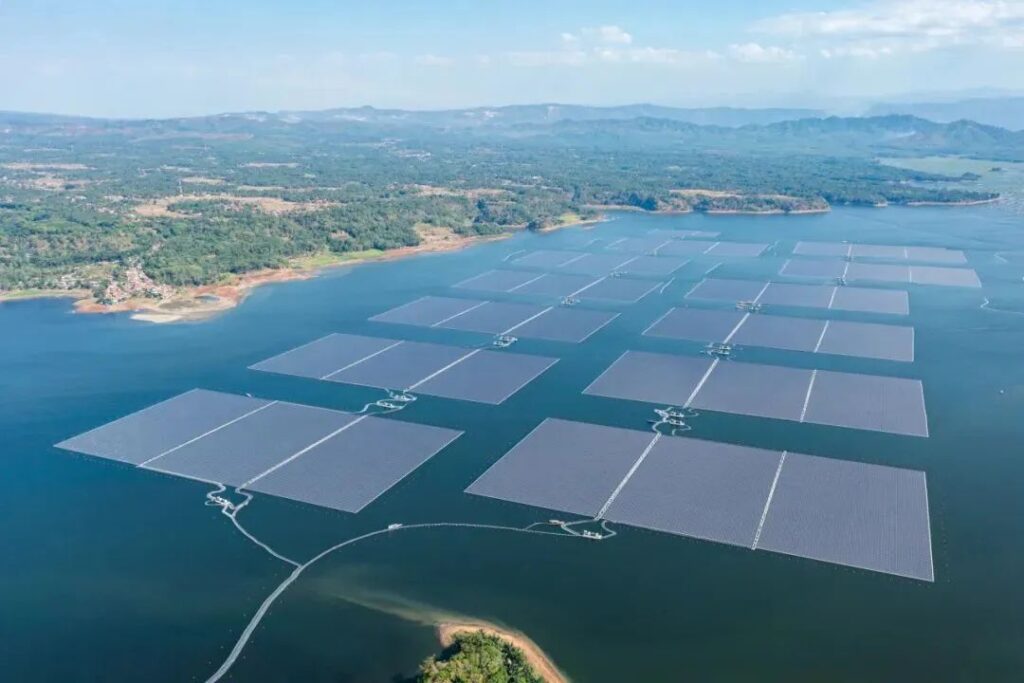
On a larger scale, solar energy is used in industrial applications where it powers manufacturing processes, large-scale water desalination plants, and even contributes to cooling and heating needs. Solar thermal power plants, for instance, use concentrated solar power systems to generate electricity for industrial operations.

Solar energy is also making inroads into the transportation sector. Solar-powered vehicles and charging stations are beginning to emerge, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Additionally, solar panels are used in various infrastructures like street lighting, traffic and railway signals, which are not only cost-effective but also environmentally friendly.
In agriculture, solar energy is used for a variety of purposes including powering irrigation pumps, ventilation systems for greenhouses, and electric fences. Solar dehydrators are used to dry crops and other agricultural products, enhancing food preservation techniques.
Solar energy plays a crucial role in providing electricity to remote areas where grid connectivity is either unreliable or non-existent. Solar panels can power telecommunications equipment, offshore navigation systems, and rural health clinics, facilitating basic amenities and services in isolated regions.
On the consumer level, solar energy is used to power a multitude of devices, from solar-powered calculators and watches to garden lighting and portable chargers. These applications highlight the adaptability of solar technology to everyday life, providing convenience while reducing energy consumption.
The diversity of applications for solar energy systems underscores their potential in contributing to sustainable development across multiple sectors. As technology advances and costs continue to decline, the scope of solar energy applications is likely to expand, further embedding solar power in the fabric of global energy solutions.
The affordability of solar energy systems has significantly improved over the past decade due to technological advancements and increased market competition. However, several factors influence the cost of installing a solar energy system.

The size of the system, typically measured in kilowatts (kW), is one of the primary determinants of cost. A larger system will generate more electricity but will also require a greater number of panels and more extensive installation work, which increases the overall cost. Residential systems generally range from 3 kW to 10 kW, while commercial installations can exceed 100 kW.
The quality and type of components used significantly impact costs. High-efficiency panels made from monocrystalline silicon are typically more expensive than their polycrystalline counterparts but offer greater efficiency in converting sunlight to electricity. Additionally, the choice of inverter, whether a string inverter or a microinverter, affects cost. Microinverters tend to be more expensive but can provide better performance in shaded conditions or for roofs with multiple orientations.
The complexity of the installation process can also influence the cost. Factors such as roof type, the angle of roof inclination, and the presence of obstacles like chimneys or skylights can affect how easy it is to install the panels. Ground-mounted systems may require additional construction work, such as cement foundations, which can further increase installation costs.
Installation costs can vary by geographic location due to differences in labor costs, the availability of solar incentives, and the average amount of sunlight. Regions with higher labor rates will generally see higher installation costs, while areas with government incentives like tax breaks or rebates may see lowered net costs.
While maintenance costs for solar energy systems are generally low, periodic cleaning and occasional repairs or replacements of components such as inverters or storage batteries must be considered. Additionally, insurance for the system may add to the operational costs.
Overall, while the initial investment for a solar energy system can be substantial, the reduction in electricity bills and potential incentives generally lead to a reasonable payback period, after which the electricity generated is virtually free.
To ensure safety, performance, and reliability, solar products undergo rigorous testing and must meet specific international standards and certifications.
Adherence to these standards not only enhances consumer trust in solar products but also facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements in various markets, paving the way for global trade and the widespread adoption of solar technology.
Recent innovations in solar technology are significantly enhancing the efficiency and application scope of solar energy systems.
Perovskite solar cells have emerged as a promising technology due to their high efficiency and low production costs. Unlike traditional silicon-based cells, perovskites are made from materials that can be processed in solution, potentially enabling simple printing techniques for manufacturing.
BIPV technology integrates photovoltaic materials directly into building structures, such as windows, facades, or roofs. This not only serves the dual purpose of building material and power generator but also enhances aesthetic value and architectural flexibility.

Organic photovoltaic cells are made from organic materials that are capable of converting light into electricity. Though currently less efficient than their silicon counterparts, OPVs can be produced in diverse colors and shapes, are lightweight, and offer flexibility in application (such as integration into wearables or portable charging devices).
Advancements in solar thermal storage technology are allowing for greater efficiency in capturing and storing solar energy. Systems like molten salt storage, where salts are heated by solar energy during the day and stored in insulated tanks, can retain heat for hours or days. This heat can then be used to generate steam and produce electricity even when the sun is not shining, addressing one of the major limitations of solar energy—its dependency on sunlight availability.
Bifacial solar panels, which capture sunlight from both sides, are increasing the efficiency of solar installations. These panels can generate more electricity compared to traditional single-faced panels, particularly in areas with high ground reflectance.
Solar inverters are also seeing significant advancements, including smart inverters that can interact more intelligently with the grid. These devices can help manage grid stability by providing ancillary services like voltage and frequency regulation.
Additionally, modern inverters are increasingly integrating with home energy management systems, allowing for smarter energy usage and optimization.
These innovations are making solar energy more viable and efficient, promising a brighter future for renewable energy technologies.

The solar energy market is experiencing robust growth globally, driven by several key trends that are shaping the industry.
Firstly, technological advancements have significantly reduced the cost of solar panels and related equipment, making solar installations more affordable for residential, commercial, and industrial users. The price reduction is a result of improvements in photovoltaic (PV) cell efficiency and manufacturing processes, coupled with economies of scale in production.
Secondly, there is a growing public and governmental awareness of the benefits of renewable energy, which has been crucial in driving the adoption of solar power. This awareness is bolstered by concerns over climate change and the environmental impact of fossil fuels. As a result, many countries have implemented supportive policies, including subsidies, tax incentives, and feed-in tariffs, which encourage the development and adoption of solar energy solutions.
Moreover, the integration of solar with other technologies such as energy storage systems is becoming more prevalent. This integration enhances the reliability and utility of solar power, allowing for energy supply even when the sun isn’t shining. Additionally, the rise of smart grid technology is facilitating the efficient distribution and management of solar energy in grid systems.
These factors collectively contribute to a dynamic expansion of the solar market, positioning solar energy as a key component of the global transition towards sustainable energy futures.
The solar industry has developed several business models to make solar energy more accessible and financially viable for different types of consumers:

In this model, consumers lease solar panels or agree to purchase the power generated by panels installed on their property.
They do not own the equipment and typically pay a fixed monthly rate that is often lower than their regular utility bill. This rate depends on the amount of electricity generated.
This model is attractive for consumers who want to reduce energy bills without a significant upfront investment.
Consumers buy the solar system outright, which means paying for the installation and equipment upfront or through financing. Ownership of the system allows consumers to benefit from all the electricity it produces without ongoing payments, other than maintenance. This model can offer the highest long-term savings and increase the property value, but it requires a larger initial investment.
Similar to direct purchase, solar loans facilitate ownership with the benefit of spreading the cost over time. Consumers finance their solar systems through loans, which they pay back over several years. Once paid off, the consumer owns the system and benefits from the free electricity it generates.
This model allows multiple people to benefit from a single, shared solar system located on-site or off-site. Participants subscribe to the community solar project and receive credit on their electricity bills for their share of the power produced.
This model can offer the highest long-term savings and increase the property value, but it requires a larger initial investment.

These diverse business models enable more consumers to participate in and benefit from solar energy, regardless of their initial capital or desire for system ownership. Each model offers distinct advantages, depending on individual financial situations, goals, and local regulatory environments.
The solar energy sector, while burgeoning, faces several challenges that need addressing to maximize its global impact.
First, further reduction in technology costs is essential. Although prices have dropped significantly, making solar more competitive, continuous investment in R&D is needed to make solar solutions even more affordable and efficient.
Second, grid integration presents a challenge. As solar penetration increases, the power grid must evolve to handle intermittent solar power, requiring sophisticated grid management technologies and regulations that support bidirectional energy flows.
Additionally, energy storage remains a critical hurdle. Effective storage solutions are crucial for balancing supply and demand, ensuring reliability, and maximizing the utilization of solar energy. Developing cost-effective, high-capacity storage technologies will be pivotal in overcoming this challenge.
On the opportunities front, solar energy holds tremendous potential in developing countries, where many regions still lack access to reliable electricity. Solar can leapfrog traditional grid infrastructure, offering a quicker, sustainable path to electrification.
Furthermore, technological innovations such as perovskite solar cells and integrated photovoltaic systems promise to enhance efficiency and adaptability.
Lastly, as global energy needs escalate, solar energy stands as a key renewable resource capable of substantially contributing to a sustainable energy future, driving economic growth, and reducing carbon emissions worldwide.

When considering the purchase of solar products, several key factors must be evaluated to ensure that you make an informed and effective decision. Here’s a comprehensive guide to some of the primary considerations:
First, assess your energy consumption. Understanding your average energy usage will help determine the size and type of solar system required to meet your needs. Check past utility bills to estimate how much power you consume and consider future changes that might increase your energy requirements.
The efficiency of solar panels, which is how well they convert sunlight into electricity, varies between models and manufacturers. Higher efficiency panels are usually more expensive but are essential in areas with limited space as they generate more power per square meter. Ensure the panels have been certified by reputable international standards to guarantee their performance and durability.
Solar systems represent a significant investment. While the upfront cost can be high, it’s important to consider long-term savings on electricity bills. Explore different financing options such as leases, loans, or Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) if upfront payment is challenging. Also, look for government incentives, subsidies, or rebates that can reduce the initial cost.

Choose products from established manufacturers with a proven track record in the industry. Research their market reputation, read customer reviews, and check their financial stability. A reliable manufacturer should offer robust warranties that cover the panels and other components for extended periods.

Professional installation is crucial to maximizing the efficiency and lifespan of your solar system. Seek out qualified and experienced installers who comply with local regulations and industry standards. Additionally, understand the maintenance requirements of your system. Although solar systems generally require minimal maintenance, regular checks will help in early detection of potential issues, thereby avoiding costly repairs.
If integrating solar power with an existing power system, ensure compatibility. This includes adequate matching with the home’s or building’s current electrical system and potential integration with other renewable energy systems.
Solar panel performance can be influenced by local weather conditions. In areas with high temperatures, solar panels can overheat, leading to reduced efficiency. Similarly, regions with frequent snowfall or dust might require additional features like self-cleaning or cooling technologies to maintain optimal performance.
Be aware of local zoning laws, building codes, and regulations regarding solar panel installations. Some regions might require special permits, or there may be restrictions on the type or size of the system you can install.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose a solar product that not only fits your energy needs but also offers reliability and efficiency over its lifetime, ultimately providing significant environmental and economic benefits.
Choosing the right solar energy supplier or manufacturer is crucial for ensuring a successful solar installation that meets your energy needs and provides reliable service for years to come. Here are key considerations to help guide your decision:
By thoroughly evaluating these aspects, you can select a solar energy supplier or manufacturer that not only provides a high-quality, efficient solar system but also supports your goals for energy independence and environmental sustainability.
While solar energy is becoming a common feature in the daily lives of many in developed countries, its adoption is still in its infancy in many remote and underdeveloped areas around the world. Despite these challenges, the global commitment to renewable energy sources and the ongoing efforts by various governments to promote and expand the accessibility of solar technology are setting the stage for a profound transformation. Solar energy is poised to become a cornerstone of global energy solutions, contributing significantly to reducing carbon footprints and fostering sustainable development.
In this evolving landscape, SolarCtrl stands out as a dedicated partner and provider in the solar industry. With a commitment to quality, innovation, and customer satisfaction, SolarCtrl offers a range of solar products that meet the highest standards of efficiency and reliability. Our products are designed to cater not only to well-developed markets but also to bring renewable energy solutions to remote areas, helping bridge the energy divide and promoting inclusivity in access to clean energy.
We invite businesses, installers, and distributors interested in making a positive impact on the environment and participating in the global shift towards renewable energy to partner with us.
Contact us today to explore how our solar solutions can benefit your business and contribute to a greener future.
Yes, we provide samples and charge for the samples with freight cost. The sample fees will be returned if the order quantity over 200pcs.
We have streamlined our production processes to ensure that most of our products are readily available in stock. This means that you can purchase samples and have them shipped at any time and without delay.
Technical support hotline or email for customers to contact in case of technical issues with our products.
Onsite technical support to assist with the installation and maintenance of the products.
Online resources such as manuals, troubleshooting guides, and FAQs to help customers resolve common issues with the products.
Warranty or guarantee period to ensure that customers are covered in case of product defects or malfunctions.
Repair and replacement services for damaged or faulty products.
To provide local technical support, we offer a range of services to VIP distributors, including installation, usage guidance, maintenance, and other related support, free of charge. For larger projects with a capacity of over 55KW, if on-site technical support is required, the cost of airfare, lodging, and meals must be covered by the distributor.
Our technical support services include system design, installation, commissioning, repair, and maintenance. We aim to provide prompt and effective technical support to ensure the smooth operation of your equipment and systems.
To optimize our technical support services, we continuously update our knowledge and skills, and we invest in the latest tools and technologies to enhance our capabilities. In addition, we strive to maintain open communication channels with our clients to ensure that their needs and concerns are addressed promptly and effectively.
Machine appearance customization: Customers can choose the style and color of the machine according to their preferences.
Logo customization: Customers can have their own logo printed on the machine to increase brand recognition.
Label customization: Customers can customize the labels on the machine to include specific information or warnings.
LCD display customization: Customers can customize the information displayed on the LCD screen to meet their specific needs.
Packaging customization: Customers can customize the packaging of the machine to suit their requirements, including the design and materials used.
For orders of less than 10 units, we generally ship within two days. For orders between 10 and 100 units, we aim to ship within one week. To ensure the quality of our products, we keep sufficient inventory and perform a final round of testing before packaging and shipping.
Please note that the delivery time may vary depending on factors such as the destination, shipping method, and customs clearance processes. We work with reliable shipping partners to ensure timely delivery and provide tracking information for all shipments.
We usually ship by DHL, UPS, FedEx, or TNT. Bulk orders can be shipped by airline or sea shipping as well. It is important to note that the choice of shipping method may depend on factors such as the size and weight of the shipment, the destination, and the urgency of the delivery.
We offer several payment methods for your convenience, including T/T, L/C, Western Union, PayPal, and cash. Please choose the payment method that works best for you.
Yes, we provide samples and charge for the samples with freight cost. The sample fees will be returned if the order quantity over 200pcs.
We have streamlined our production processes to ensure that most of our products are readily available in stock. This means that you can purchase samples and have them shipped at any time and without delay.
Technical support hotline or email for customers to contact in case of technical issues with our products.
Onsite technical support to assist with the installation and maintenance of the products.
Online resources such as manuals, troubleshooting guides, and FAQs to help customers resolve common issues with the products.
Warranty or guarantee period to ensure that customers are covered in case of product defects or malfunctions.
Repair and replacement services for damaged or faulty products.
To provide local technical support, we offer a range of services to VIP distributors, including installation, usage guidance, maintenance, and other related support, free of charge. For larger projects with a capacity of over 55KW, if on-site technical support is required, the cost of airfare, lodging, and meals must be covered by the distributor.
Our technical support services include system design, installation, commissioning, repair, and maintenance. We aim to provide prompt and effective technical support to ensure the smooth operation of your equipment and systems.
To optimize our technical support services, we continuously update our knowledge and skills, and we invest in the latest tools and technologies to enhance our capabilities. In addition, we strive to maintain open communication channels with our clients to ensure that their needs and concerns are addressed promptly and effectively.
Machine appearance customization: Customers can choose the style and color of the machine according to their preferences.
Logo customization: Customers can have their own logo printed on the machine to increase brand recognition.
Label customization: Customers can customize the labels on the machine to include specific information or warnings.
LCD display customization: Customers can customize the information displayed on the LCD screen to meet their specific needs.
Packaging customization: Customers can customize the packaging of the machine to suit their requirements, including the design and materials used.
For orders of less than 10 units, we generally ship within two days. For orders between 10 and 100 units, we aim to ship within one week. To ensure the quality of our products, we keep sufficient inventory and perform a final round of testing before packaging and shipping.
Please note that the delivery time may vary depending on factors such as the destination, shipping method, and customs clearance processes. We work with reliable shipping partners to ensure timely delivery and provide tracking information for all shipments.
We usually ship by DHL, UPS, FedEx, or TNT. Bulk orders can be shipped by airline or sea shipping as well. It is important to note that the choice of shipping method may depend on factors such as the size and weight of the shipment, the destination, and the urgency of the delivery.
We offer several payment methods for your convenience, including T/T, L/C, Western Union, PayPal, and cash. Please choose the payment method that works best for you.

*All your information will be kept strictly confidential and our business staff will ensure that your private information is absolutely safe!

Solarctrl is a professional solar energy manufacturer integrating R&D, production, and export. We provide high-performance solar panels, inverters, lithium batteries, and energy storage systems for global distributors and installers.
Get interesting news
Subscribe to receive the latest updates on solar technology, market insights, and product releases — tailored for solar distributors and installers worldwide.
2025 Solarctrl. All rights reserved.

Emily
Typically replies within minutes
Any questions related to solar energy products?
WhatsApp Us
🟢 Online | Privacy policy
WhatsApp us



REQUEST A QUOTE
*Your email information is completely secure and will not be disclosed to third parties for any reason.

REQUEST A QUOTE
*Your email information is completely secure and will not be disclosed to third parties for any reason.

No middlemen. Get competitive pricing directly from a trusted solar panel manufacturer in China.
All panels are tested and certified to CE, TUV, IEC standards—ready for your local market.
Start small or scale up—we support your business with low minimum order quantities.
Stable stock and efficient logistics ensure on-time global shipping, even for urgent projects.
Our expert team offers responsive service, clear documentation, and technical guidance at every step.
Fill out the form below to get our free product catalog—including detailed specs, certifications, and pricing info.
Start sourcing smarter with high-efficiency, certified solar products direct from the manufacturer.